Before the publication of Adam Smiths’ influential work “An Enquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations” in 1776, there were two popular doctrines that had a huge influence on public policy. The first doctrine was a mercantilist doctrine that emerged roughly 200 years prior to Adam Smith. The mercantilist doctrine did influence public policies in favor of international trade. Mercantilists advocated for government intervention and regulation in the favor of international trade. Such doctrine had ruled around 150 years before Adam Smits’s classic work. After Mercantilism there emerged another influential doctrine called physiocracy for not more than roughly 30 years. That particular doctrine had emerged in France and is considered more organized and scientific than the methodology of mercantilism.
Contents
Meaning of Mercantilism and its Methodology
Mercantilism was one of the dominant economic thoughts or system of trade emerged between 1500 and 1800. This doctrine especially emerged from western Europe and specifically from England. Other involved countries were Holland, France, Spain, Italy, Germany, Austria, etc.
Mercantilists did not signify any particular and organized group of thinkers or philosophers rather it denoted different persons living in different countries of Europe but some way or the other they were representing the trade interest and they all had a common desire to have a strong nation-state and get the release from feudalism.
The name mercantilists were given later on by Adam Smith. The doctrine was known by different names in different countries. In England, it was known as Mercantilism, Colbertism in France by their Finance Minister, Cameralism in Germany.
The countries involved in the practice of mercantilism wanted to have a strong nation and for such, they wanted fewer imports and more exports to accumulate more gold and silver. Mercantilism powered the evolution of nation-states out of the ruins of feudalism. Mercantilism was called the economic counterpart of political nationalism.
Objectives/Goals
Mercantilism doctrine had the following major objectives
To generate trade surplus as much as possible (by exporting more and importing less)
To build strong and self-sustained nation-states
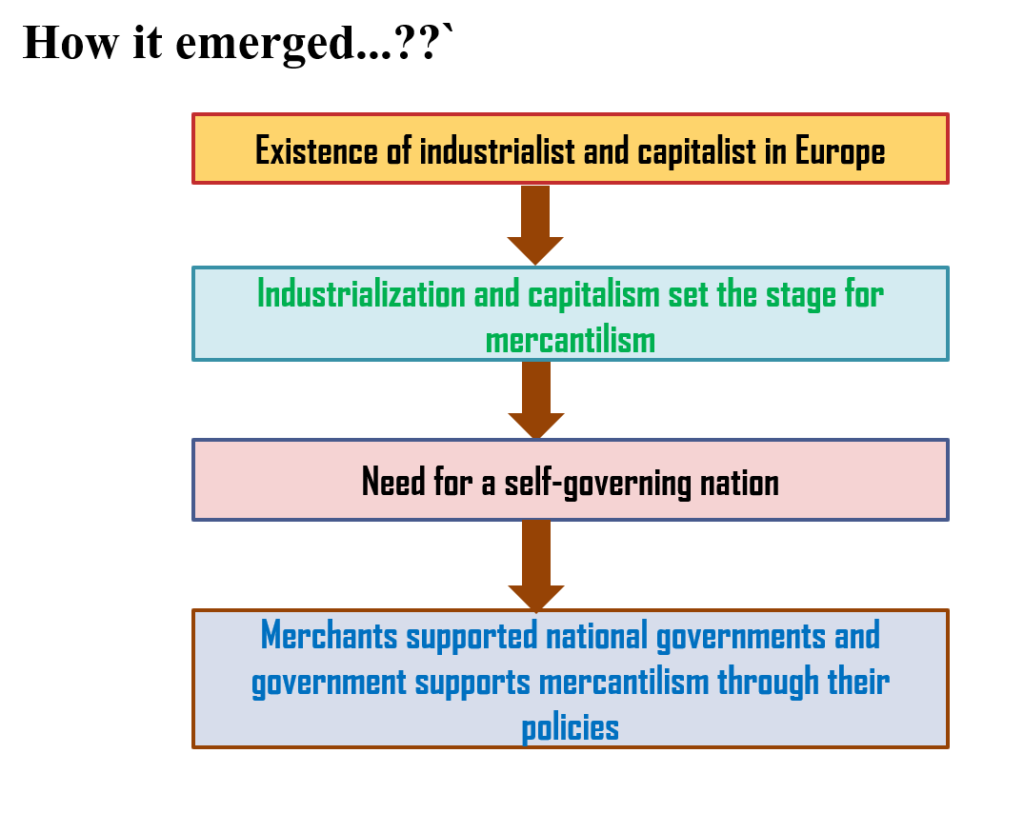
Scenario: Context in Which Mercantilism Emerged
- Agriculture was there as the primary sector in all the countries.
- Industrialists and capitalists were busy doing their manufacturing business in a small volume and within small areas.
- Economies were transforming from barter to exchanged economies or monetized economies. With such transformation value and importance of money, precious metals like gold and silver and the market had increased more.
- Europe was in the ending stage of rule by the church and feudal lords (feudalism) and increasing enlightenment, renascence, inventions, and as a result there was rising commercial capital (production was excess than consumption). All these things demanded new opportunities and inventions.
- 1492 was the year that Columbus discovered America.
- Invention and use of the compass had given expansion and discovery of Maritime routes, and improving navigation vessels
In such a context different thinkers in different places of Europe were advocating favorable foreign trade and strong state-nations.
Ways Used to Accomplish the Stated Objectives and Interests
Transformation of economies from the barter to exchange had invited to change in techniques of production, factor employment, as well as concepts of the market in Europe.
Apart from this fact, the above-mentioned factors also contributed to the building of a new market and a strong nation-state. They found that the accumulation of treasure or precious metals (gold and silver) through positive and surplus international trade or foreign trade was the major means of building a strong nation-state.
Policy Prescriptions by Mercantilism
- They advocated for the need for strong government regulation and policies especially trade policies and regulations in order to make it positive or surplus and to accumulate gold and silver as much as possible.
- They advised the government to concentrate on manufacturing sectors rather than the agriculture sector as they thought that agriculture would not be able to generate exportable surplus out of consumption. They highly advocated manufacturing sectors.
- At the same time, they also prescribed the government to discourage the usuries practices and to form new laws and rules to provide required capital for expansion of trade and investment in manufacturing sectors.
So, the government did and implemented all these prescriptions of mercantilists as they also wanted to build strong nation-states and get a release from the rule of feudal lords.
Mercantilism had thus known as the economic component of political nationalism. Thus, it is said that mercantilism had ruled and influenced the public policy discourses entirely more than 200 years before the emergence of classical economic thought.
What European Governments Did?
Following are the major steps that the European governments had taken to implement the doctrine of mercantilism;
- Limits and restrictions on imports- tariff barriers (trade between certain countries or geographical areas which take the form of abnormally high taxes charged by the government on imports), quotas, or non-tariff barriers.
- Primarily concentred themselves on gathering foreign currency reserves, and gold and silver. The prosperity and progress of the nation were measured on the attainment and stock of precious metals and foreign exchange reserves during that time. It was known as bullionism.
- The government had provided and granted monopoly power to particular firms especially those related to manufacturing, trade, and delivery(shipping).
- They had granted subsidies and support packages to exporting firms and industries so that they could gain a competitive advantage in the global market (tax exemption to exporting and import-substituting industries.)
- The government had invested and elaborated huge in research and development activities to gain more efficiency and to build and restructure the capability of the home manufacturing units and industries.
- The government had allowed copyright to national and domestic corporations and industries to avoid intellectual stealing from overseas.
- They implemented wage limiting policies for the workers to limit their consumption so that it was possible to allow larger profits would remain with the capitalist/merchants’ class.
- They applied highly controlled policies for their colonies. They made it was compulsory for their colonies to purchase products only from the domain countries.
- They had full control over the wealth and resources of colonies.
Cases of Mercantilism: Examples
- England Navigation Act of 1651 banned external (foreign) vessels and containers engaging in coastal trade.
- In 1651, Oliver Cromwell’s Parliament took steps to block and weaken the primacy of the Dutch who were acting as a kind of ‘storehouse’ for goods from all over the world and running trade to England and elsewhere in Europe.
- They made the rule that all colonies that export to Europe needed to pass through England first and then only re-exported to Europe.
- After the restoration of Charles II, Parliament continued this policy of protecting the English trade. New legislation approved in 1660, 1662, and 1663 trade between England and her colonies was efficiently restricted to English shipping.
- Under 18th century legislation, certain colonies’ exports such as sugar, rice, and tobacco had to be shipped first to England before they could be re-exported to European ports.
- Duties were charged after products were landed in England.
- The Navigation Laws backed a framework of protection for trade that lasted until the middle of the 19th century.
- Under the British Empire, India was controlled in buying from domestic industries and was enforced to import salt from the UK.
- In the 17th century, the finance minister of France J.B. Colbert named mercantilism Colbertism and advocated the state-regulated controlled economy with strong regulation about the economy and labor market.
How did Mercantilism fail?
Every idea and doctrine is always relevant to the time. They are relevant means they are able to solve the problems of issues that emerged at a particular point in time. If the ideas and principles are failed to answer and guide the contemporary of the emerging questions of the matter then they usually become outdated and finally failed.
Mercantilism had dominated public policy formulation in Europe very strongly for more than 200 years. All the West European countries had followed such doctrine in their policies and extensively involved themselves in the international trade based on zero-sum game policy. This all had raised the commercial capital and industrial capital in the European economies. High accumulation of industrial capital needed the release of government intervention and regulation. That has created a contradiction in the policies of the government and the need for capitalists. The main factors that lead to the failure of mercantilism are pointed as;
- Excessive accumulation of industrial capital needed less government intervention and open markets
- Rise of Physiocracy in France in the 18th century (roughly 1750-1780) and advocated for the natural order and the free market.
- In 1776 Adam Smith with the publication of the Wealth of Nations advocated the invisible hand. He had introduced the theory of absolute cost advantage against the zero-sum game of foreign trade. Smith had also reasoned the paybacks of free trade and criticized the wastefulness of monopoly.
- David Ricardo also criticized the monopoly trade through his theory of comparative advantages.
- Mercantilism forced government regulation and monopoly and ultimately both lead to inefficiency and corruption.
- Mercantilism had encouraged colonization.
- Mercantilism leads to a rivalry between countries participating in international trade.
- No possibility of specialization and economies of scale in mercantilism and governmental control.
- The emergence and growth of globalization and free trade during the post-war period
- Rise of protectionist policies following the great depression; countries required to reduce imports and also reduce the value of the currency.
These all lead to gradually weakening the doctrine of mercantilism and ultimately being replaced by capitalism.
Neo-Mercantilism or Modern Mercantilism
Neo-mercantilism or modern mercantilism can be seen as the tread surplus of economically and politically powerful countries like China and the USA. Neo-Mercantilism parallels political control with economic power and economic power with a balanced trade surplus. It is designed to limit imports, capital movement, and boost exports. For example, keeping undervaluation of domestic currency against other powerful currencies to discourage imports from such countries and boosting export.
Neo-mercantilism can be seen in the form of the purchase of foreign currency assets by the domestic government to retain the exchange rate undervalued and make exports more competitive and reduce imports. It can be seen more in centrally planned communist countries like Russia, China, etc. As a result, China has been the largest owner of US debt. The government also provides subsidies to the industry to gain an unfair advantage.
China has been accused of offering state-supported subsidies for industry, leading to an oversupply of industries such as steel- meaning other countries struggle to come. There is an increasing trade war between the USA and China in order to protect their products and dominate their political as well as economic will. They may have felt that they would lose their domination with free flow of goods and in order to keep their BOP favorable and surplus US tariffs on Chinese imports and in return China does the same. The dumping practice of China is also considered modern mercantilism.
References
Ideal Coaching. Mercantilism Theory of Trade. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M4aGy4G-Yoc&t=906s
Tejvan Pettinger. Mercantilism theory and examples. Retrieved from https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/17553/trade/mercantilism-theory-and-examples
E.Z Classes. Mercantilism. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rimtFx-1Zvo&t=123s