At a general level, the idea of profit would emerge very clearly as Profit is the difference between revenues and costs. On nearer assessment, however, one must be vigilant to make a distinction between two definitions of profit; economic profit and accounting or business profit. The relationship between economic and business profit can be explained below.
Contents
Business or Accounting Profit
The term profit in economics differs from that generally used by the business community. A business profit or an accounting profit or accounting concept of profit presents the residual sales revenue to the owners of the business firms after making payments to all purchased factors or resources used by the firm belonging to other persons.
These payments to purchase factors include the wages to hired labor, interest to borrowed capital, rent on land and factory buildings, and expenditure on raw materials used by the firms and are called explicit costs.
The accounting aspect defines profit as the remaining part of sales revenue after deduction of explicit cost or out-of-pocket expenditures of doing business. It is the amount available to provide rewards to the shareholders who have supplied the firm’s equity capital after payment of all other resources the firm has used in the production process. Thus, explicit costs are the cost like wages, rent, fuel, raw material, interest on loan and depreciation, etc.
Business/ Accounting profit= Total sales proceed- Explicit cost/ out-of-pocket expenditures
Where explicit cost is the payment made to those factors by the business firm which is hired by others or which are not in the ownership of the producers. Thus, the cost incurred on haring external factors used in production is called explicit cost.
Economic Profit
Economic profit is an excess of revenue over the cost of doing any business. Here the cost of business includes explicit as well as implicit both types of costs. It means economists include the implicit costs of factor inputs provided by the owners including entrepreneurial effort and skill, capital in the calculation of profit.
So, it is the difference between total revenues and total economic cost (including the economic or opportunity cost of owner-supplied resources such as capital and time). Here opportunity cost is the highest valued alternative opportunity that must be sacrificed as a result of choosing an alternative.
The owner may use his own capital for which he or she should be paid. The ordinary rate of return on capital should be given to the owner as of the minimum return necessary to attract and continue investment and in the same way, the opportunity cost of the owner’s effort is ascertained by the value that could be received in an alternative activity. Hence economic profit is business profit minus the implicit cost of the firm.
Economic profit = Sales proceed- total cost or total economic cost = Sales proceed- explicit cost-implicit/opportunity/imputed cost
Where implicit cost is the cost for the factors supplied by the owner-entrepreneur himself for the production in his own firm.
Therefore, accounting cost is the monetary value of the payment made to the externally owned factors of production contributing to business production.
The concept of accounting cost is useful in the process of calculation of a firm’s profit/loss state but not significant if the duty is to take the decision. Accounting cost only includes historical cost but the decision-making record of future cost is also necessary, which accounting or business cost is not able to include in their calculation.
On the alternative side, economic cost includes both explicit as well as implicit costs to calculate the actual cost of business doing. Economic costs are higher than accounting costs by the amount of opportunity cost or implicit cost or imputed cost.
Entrepreneurs always have to estimate the implicit cost to take business decisions and to engage in any particular business.
Thus Economic Cost= Accounting cost + Implicit Cost
Or
Economic Cos= Explicit Cost + Implicit Cost
Here the economic cost comes with the inclusion of future cost and future profit so it is to be considered while decision making is the issue.
Therefore,
Economic Profit= Accounting Profit- Implicit/Opportunity Cost
Or
Economic Profit= Sales revenue- explicit cost- implicit cost
The amount of economic profit is always lower than the amount of accounting profit by the amount of implicit const. So, there exists a deep relationship between economic and business or accounting profit.
Economic Profit VS Accounting Profit
The major differences between economic and accounting profit are shown below;
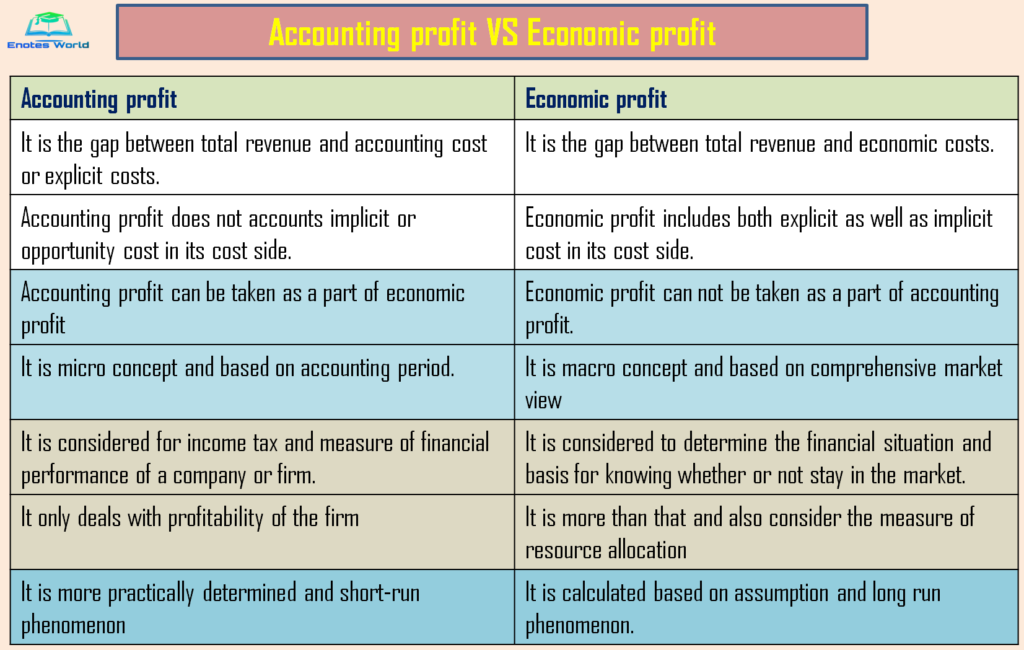
Concluding remarks on the relationship between economic and business profit
Whatever is the type of profit, it is the most significant concept in business management. It is taken as the key measure of a successful business. Classical economists have taken it as the sole objective of the firm. But post-classical economists have focused on other major issues as the goal and objectives of the firm along with profits.
So the future of the company is based on the profitability ratio and its management in the present time and the potentiality of earning profit in the near future. Shareholders of the company may prefer accounting profit over economic profit in order to get the actual and factual financial position of the firm. For the analyst, only the account of business profit is not desirable. So there is a relationship between economic and business profit and profit is the lifeblood of each of the organizations. It has several crucial functions in the business organization.
Measurement of Accounting and Economic Profit
Here are some practical cases for the calculation of accounting and economic profit. (Relationship between economic and business profit mathematically)
Case-I
A technician leaves a job having a salary of Rs. 360,000 annually to start his own business. He is ready to invest Rs. 480,000 deposited in the bank that yields a 5 % interest rate annually. He thinks to use his own house rented Rs. 1500 per month. The revenue in the first year looks to be Rs. 130,000 per month and estimated expenditures are;
| Advertisement | Rs. 4000/month |
| Taxes | Rs. 5,000/month |
| Employee salary | Rs. 50,000/month |
| Supply of materials | Rs. 15,000/month |
| Utilities | Rs. 2,000/month |
Required: Accounting profit, Economic profit, and Suggest whether starting a new business is beneficial or not to him.
Solution:
Here given, explicit costs are;
| Advertisement | Rs. 4000/month |
| Taxes | Rs. 5,000/month |
| Employee salary | Rs. 50,000/month |
| Supply of materials | Rs. 15,000/month |
| Utilities | Rs. 2,000/month |
| Total explicit cost | Rs. 76,000/month |
Implicit costs are;
| Monthly salary foregone | Rs. 360,000/12= Rs. 30,000/month |
| Interest foregone | (5 % of Rs. 480,000)/12= Rs. 2000/month |
| Rent foregone | Rs. 1500/month |
| Total implicit cost | Rs.33,500 /month |
Estimated total revenue= Rs. 130,000
Now,
Calculation of Business profit:
Business profit= Sales revenue- total explicit costs =Rs. 130,000- 76000 = Rs. 54,000/month.
Hence the amount of business/accounting profit is Rs. 54,000 per month.
Calculation of Economic profit:
Economic profit= Sales revenue- economic costs = Sales revenue- (explicit cost+ implicit cost) = Rs. 130,000- (76,000+33,500) = Rs. 20,500.
Hence, the value of economic profit is Rs. 20,500 per month.
Here the value of economic profit is positive by Rs. 20,500. It means he can earn more by Rs. 20,500 if he starts his own business rather than engaging in any company. So the suggestion is better to leave the existing job and start own new business.
Case-II
Robert, a web designer working as a web developer in a company for Rs. 120,000 per year wants to start his own business by investing his own money of Rs. 400,000 on which he could earn 10 % interest if deposited in a bank. His estimated earnings during the first year are Rs. 300,000 and costs are; 90,000 salaries to staff, supplies cost Rs. 30,000, rental expenditure is Rs. 20,000 and for utility Rs. 2,000.
Then, by how much amount there is a difference in accounting and economic profit. Give him the advice to start or not the new business as an economic analyst. What will be your advice if he could earn only 2 percent interest on his own money if he deposited it in a bank.
Solution:
Determining implicit cost
So, Implicit cost= Salary foregone + Interest foregone= Rs. 120,000 + Rs. 40,000 =Rs. 160,000.
Determining explicit cost
So, Explicit cost= Salary to employee + Supplies + Rent + Utilities = Rs. 90,000 + Rs. 30,000 + Rs. 20,000 + Rs. 2000 = Rs. 142,000
Total revenue= Rs. 300,000
Now
Business Profit= Rs. 300,000- Rs. 142,000= Rs. 158,000
Economic Profit= Rs. 300,000- (142,000+160,000) = Rs. -2000
Here accounting or business profit is positive or Rs. 158,000 but economic profit is negative or Rs (2000). This means Robert could earn Rs. 2000 more if he continues his job rather than starting a new business.
Again,
If Robert could earn interest of 2% on his own money than implicit cost will be= Salary foregone + Interest foregone = Rs. 12,000 + Rs. 8,000= Rs. 128,000
So economic profit= Rs. 300,000- Rs (142,000+ 128000) = Rs. 30,000.
Here the value of economic profit is Rs. 30,000 at an interest rate @2 % per annum. Therefore, in such a case, Robert can earn positive economic profit by starting his own business rather than staying in a previous job. So, the suggestion is to start a new business than continue the existing job and invest in the bank.
Case-III
An engineer sacrifices the job of having a salary of Rs.30, 000 annually to initiate his own business. He thinks to invest Rs. 50,000 deposited in the bank that yields a 7 % interest per year. Similarly, he thinks to use his own house rented in Rs. 1500 per month. The revenue in the first year seems to be Rs. 107,000 and estimated expenses are as follows;
| Advertisement | Rs. 5000 |
| Taxes | Rs. 5000 |
| Supply of materials | Rs. 5000 |
| Rent | Rs. 10,000 |
| Employee salary | Rs. 40,000 |
Find out: Accounting profit and economic profit.
{Hints: Explicit Cost= Rs. 5000 + 5000 + 5000 + 10,000 + 40,000= Rs. 65,000 and Implicit Cost= Rs. Rs. 30,000 + 0.07*50,000 + 1500*12= Rs. 51,500)
Case-IV
An individual working as a supervisor at Everest Bank Ltd for Rs. 20,000 per month wants to start his own business by investing his own money of Rs. 600,000 and he can earn 8 % of annual interest if he deposited it into the bank. His estimated revenue during the first year of operation is Rs. 400,000 and costs are; salaries to staff Rs. 150,000; supplies Rs. 80,000; rent Rs. 60,000; and utilities Rs. 15,000. Calculate the amount of business profit, economic profit, and if he seeks your advice on whether to stay in the business or not, what will be your advice and why?
{Hints: Implicit cost= (Rs. 20,000*12= Rs. Rs. 240,000) + (0.08*600,000) = Rs. 2, 88,000 and Explicit cost= Rs. 150,000 + Rs. 80,000+ Rs. 60,000 + Rs. 15,000= Rs. 305,000)}
Like!! I blog frequently and I really thank you for your content. The article has truly peaked my interest.
Very informative. Though there are a lot of typos.
Thank You!